Sustainable Home Design: Guide To Eco-Friendly and Stylish Solutions for Your Home
Understanding Sustainable Home Design
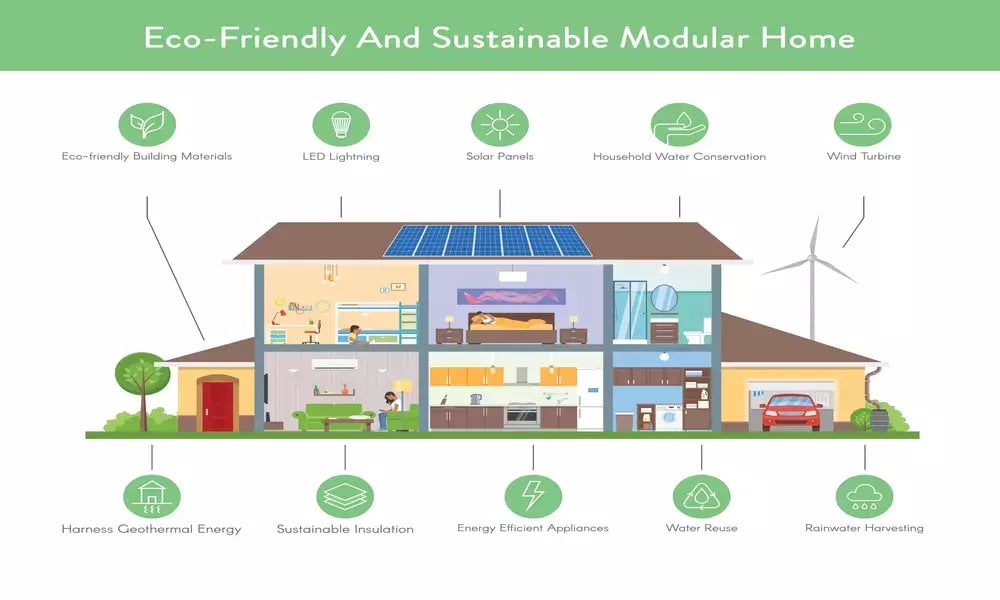
Sustainable home design refers to an architectural and construction approach focused on minimizing resource consumption, reducing emissions, and improving the environmental performance of a building. It includes energy-efficient systems, eco-friendly materials, water conservation features, and passive design strategies like maximizing natural light and ventilation.
Unlike conventional homes, sustainable homes consider the entire lifecycle of the materials used and the long-term environmental effects of daily living. From solar panels and rainwater harvesting to bamboo flooring and recycled insulation, sustainable design choices can be both practical and stylish.
Why Sustainable Home Design Matters
Sustainable design is not just a trend—it’s a response to some of the most urgent global challenges:
-
Climate Change Mitigation: Residential buildings contribute significantly to global carbon emissions through heating, cooling, and electricity use. Sustainable homes help lower these emissions.
-
Resource Efficiency: Sustainable design emphasizes using fewer natural resources and promotes recycling and renewable energy.
-
Healthier Living Spaces: Homes built with non-toxic materials and improved indoor air quality support better physical and mental health.
-
Lower Operating Costs: Over time, energy-efficient appliances, solar power, and insulation can reduce utility bills substantially.
-
Resilience and Value: Sustainable homes are more resilient to environmental extremes and increasingly sought after in the real estate market.
These benefits impact homeowners, renters, builders, and communities alike, helping address broader issues such as urban air quality, water scarcity, and waste generation.
Recent Trends in Sustainable Home Design (2024–2025)
In the past year, several trends and innovations have gained attention in the field of eco-conscious home building:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Thermostat Adoption | Intelligent systems that adapt heating/cooling based on usage and weather. |
| Solar Integration on Rooftops | Declining costs and improved efficiency have made rooftop solar more common. |
| Passive House Movement Expansion | A global increase in demand for ultra-energy-efficient Passive House design. |
| Natural Materials Usage | Growing use of hempcrete, cork, bamboo, and recycled steel. |
| Water-Saving Fixtures | More installations of low-flow faucets, dual-flush toilets, and greywater systems. |
In 2024, the World Green Building Council emphasized climate-resilient building practices, and countries like Germany, Japan, and Australia reported record investments in net-zero housing projects. Even in emerging economies, green certifications like LEED, BREEAM, and IGBC saw increased adoption.
Government Policies and Building Codes
Governments around the world have introduced policies and codes to encourage or enforce sustainable building practices. These vary by country but share common goals:
India
-
Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC): Mandates minimum energy performance standards for new buildings.
-
Star Rating System for Homes (BEE): Rates the energy efficiency of residential buildings.
-
Green Building Incentives: Several local municipalities offer fast-track approvals or property tax rebates for green-certified homes.
United States
-
Inflation Reduction Act (2022): Offers tax credits for energy-efficient appliances and home improvements through 2032.
-
Energy Star Program: Certifies products and homes that meet energy efficiency criteria.
-
State-Level Codes: States like California enforce stringent energy-efficiency standards (Title 24).
European Union
-
EPBD Directive (Updated 2023): Requires all new buildings to be zero-emission by 2030.
-
Green Deal Program: Financial support for home energy retrofits across EU nations.
Australia
-
National Construction Code (NCC): Incorporates sustainability benchmarks.
-
NatHERS (Nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme): Provides a star rating for home energy efficiency.
Such regulations support homeowners with guidance, funding, and accountability in achieving sustainability.
Helpful Tools and Resources
For those looking to make informed decisions on sustainable home design, there are a wide range of accessible tools and platforms:
| Tool/Resource | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Energy Star Home Advisor | U.S.-based tool that gives personalized home improvement tips. |
| EcoHome Network | Offers articles, checklists, and green building certification support. |
| LEED Certification Guide (USGBC) | Information on how to design and certify a green home. |
| WattBuy or EnergySage | Compare renewable energy options and providers. |
| Home Carbon Calculator (CoolClimate) | Calculates a household’s carbon footprint and reduction strategies. |
| IGBC & GRIHA Portals (India) | Indian-specific green building certification and rating support. |
| Houzz Green Home Ideas | Visual inspiration and product recommendations for eco-friendly interiors. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the key features of a sustainable home?
Key features include energy-efficient lighting and appliances, solar panels, high-performance insulation, water-saving fixtures, and the use of recycled or non-toxic materials.
2. Is building a sustainable home more expensive?
While upfront costs may be slightly higher (typically 5–15% more), long-term savings on energy and water bills often outweigh the initial investment. Financial incentives and tax credits can also reduce the burden.
3. Can I make my existing home more sustainable without a full renovation?
Yes. Simple upgrades like switching to LED lighting, using low-VOC paints, adding insulation, installing smart thermostats, and replacing old appliances with energy-efficient models can significantly improve sustainability.
4. Are there any certifications for sustainable homes?
Yes. Globally recognized certifications include LEED, BREEAM, Passive House, IGBC, and GRIHA. These provide frameworks and benchmarks for sustainability performance.
5. How does sustainable design impact indoor air quality?
Sustainable homes often use natural ventilation, non-toxic materials, and air purification systems, leading to reduced exposure to allergens, pollutants, and chemicals. This results in a healthier indoor environment.
Conclusion
Sustainable home design is more than a lifestyle choice—it’s a vital step toward creating healthier communities and protecting the environment. With growing support from governments, advancements in green technology, and increased public awareness, transitioning to an eco-friendly home has never been more practical or impactful.
By combining function, form, and responsibility, sustainable homes offer a compelling path forward—where living spaces not only look good but also do good. Whether you’re taking small steps or planning a major upgrade, every decision counts.
